READING PASSAGE 1
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below.
Crop-growing skyscrapers
By the year 2050, nearly 80% of the Earth’s population will live in urban centres. Applying the most conservative estimates to current demographic trends, the human population will increase by about three billion people by then. An estimated 109 hectares of new land (about 20% larger than Brazil) will be needed to grow enough food to feed them, if traditional farming methods continue as they are practised today. At present, throughout the world, over 80% of the land that is suitable for raising crops is in use. Historically, some 15% of that has been laid waste by poor management practices. What can be done to ensure enough food for the world’s population to live on?
The concept of indoor farming is not new, since hothouse production of tomatoes and other produce has been in vogue for some time. What is new is the urgent need to scale up this technology to accommodate another three billion people. Many believe an entirely new approach to indoor farming is required, employing cutting-edge technologies. One such proposal is for the ‘Vertical Farm’. The concept is of multi-storey buildings in which food crops are grown in environmentally controlled conditions. Situated in the heart of urban centres, they would drastically reduce the amount of transportation required to bring food to consumers. Vertical farms would need to be efficient, cheap to construct and safe to operate. If successfully implemented, proponents claim, vertical farms offer the promise of urban renewal, sustainable production of a safe and varied food supply (through year-round production of all crops), and the eventual repair of ecosystems that have been sacrificed for horizontal farming.
It took humans 10,000 years to learn how to grow most of the crops we now take for granted. Along the way, we despoiled most of the land we worked, often turning verdant, natural ecozones into semi-arid deserts. Within that same time frame, we evolved into an urban species, in which 60% of the human population now lives vertically in cities. This means that, for the majority, we humans have shelter from the elements, yet we subject our food-bearing plants to the rigours of the great outdoors and can do no more than hope for a good weather year. However, more often than not now, due to a rapidly changing climate, that is not what happens. Massive floods, long droughts, hurricanes and severe monsoons take their toll each year, destroying millions of tons of valuable crops.
The supporters of vertical farming claim many potential advantages for the system. For instance, crops would be produced all year round, as they would be kept in artificially controlled, optimum growing conditions. There would be no weather-related crop failures due to droughts, floods or pests. All the food could be grown organically, eliminating the need for herbicides, pesticides and fertilisers. The system would greatly reduce the incidence of many infectious diseases that are acquired at the agricultural interface. Although the system would consume energy, it would return energy to the grid via methane generation from composting nonedible parts of plants. It would also dramatically reduce fossil fuel use, by cutting out the need for tractors, ploughs and shipping.
A major drawback of vertical farming, however, is that the plants would require artificial light. Without it, those plants nearest the windows would be exposed to more sunlight and grow more quickly, reducing the efficiency of the system. Single-storey greenhouses have the benefit of natural overhead light; even so, many still need artificial lighting.
A multi-storey facility with no natural overhead light would require far more. Generating enough light could be prohibitively expensive, unless cheap, renewable energy is available, and this appears to be rather a future aspiration than a likelihood for the near future.
One variation on vertical farming that has been developed is to grow plants in stacked trays that move on rails. Moving the trays allows the plants to get enough sunlight. This system is already in operation, and works well within a single-storey greenhouse with light reaching it from above: it Is not certain, however, that it can be made to work without that overhead natural light.
Vertical farming is an attempt to address the undoubted problems that we face in producing enough food for a growing population. At the moment, though, more needs to be done to reduce the detrimental impact it would have on the environment, particularly as regards the use of energy. While it is possible that much of our food will be grown in skyscrapers in future, most experts currently believe it is far more likely that we will simply use the space available on urban rooftops.
Questions 1-7
Complete the sentences below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Indoor farming
1 Some food plants, including……………… are already grown indoors.
2 Vertical farms would be located in………………, meaning that there would be less need to take them long distances to customers.
3 Vertical farms could use methane from plants and animals to produce………………..
4 The consumption of………………… would be cut because agricultural vehicles would be unnecessary.
5 The fact that vertical farms would need……………….. light is a disadvantage.
6 One form of vertical farming involves planting in……………….. which are not fixed.
7 The most probable development is that food will be grown on………………… in towns and cities.
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 Methods for predicting the Earth’s population have recently changed.
9 Human beings are responsible for some of the destruction to food-producing land.
10 The crops produced in vertical farms will depend on the season.
11 Some damage to food crops is caused by climate change.
12 Fertilisers will be needed for certain crops in vertical farms.
13 Vertical farming will make plants less likely to be affected by infectious diseases.
READING PASSAGE 2
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 14-26 which are based on Reading Passage 2 below.
The Falkirk Wheel
A unique engineering achievement
The Falkirk Wheel in Scotland is the world’s first and only rotating boat lift. Opened in 2002, it is central to the ambitious £84.5m Millennium Link project to restore navigability across Scotland by reconnecting the historic waterways of the Forth & Clyde and Union Canals.
The major challenge of the project lays in the fact that the Forth & Clyde Canal is situated 35 metres below the level of the Union Canal. Historically, the two canals had been joined near the town of Falkirk by a sequence of 11 locks – enclosed sections of canal in which the water level could be raised or lowered – that stepped down across a distance of 1.5 km. This had been dismantled in 1933, thereby breaking the link. When the project was launched in 1994, the British Waterways authority were keen to create a dramatic twenty-first-century landmark which would not only be a fitting commemoration of the Millennium, but also a lasting symbol of the economic regeneration of the region.
Numerous ideas were submitted for the project, including concepts ranging from rolling eggs to tilting tanks, from giant seesaws to overhead monorails. The eventual winner was a plan for the huge rotating steel boat lift which was to become The Falkirk Wheel. The unique shape of the structure is claimed to have been inspired by various sources, both manmade and natural, most notably a Celtic double headed axe, but also the vast turning propeller of a ship, the ribcage of a whale or the spine of a fish.
The various parts of The Falkirk Wheel were all constructed and assembled, like one giant toy building set, at Butterley Engineering’s Steelworks in Derbyshire, some 400 km from Falkirk. A team there carefully assembled the 1,200 tonnes of steel, painstakingly fitting the pieces together to an accuracy of just 10 mm to ensure a perfect final fit. In the summer of 2001, the structure was then dismantled and transported on 35 lorries to Falkirk, before all being bolted back together again on the ground, and finally lifted into position in five large sections by crane. The Wheel would need to withstand immense and constantly changing stresses as it rotated, so to make the structure more robust, the steel sections were bolted rather than welded together. Over 45,000 bolt holes were matched with their bolts, and each bolt was hand-tightened.
The Wheel consists of two sets of opposing axe-shaped arms, attached about 25 metres apart to a fixed central spine. Two diametrically opposed water-filled ‘gondolas’, each with a capacity of 360,000 litres, are fitted between the ends of the arms. These gondolas always weigh the same, whether or not they are carrying boats. This is because, according to Archimedes’ principle of displacement, floating objects displace their own weight in water. So when a boat enters a gondola, the amount of water leaving the gondola weighs exactly the same as the boat. This keeps the Wheel balanced and so, despite its enormous mass, it rotates through 180° in five and a half minutes while using very little power. It takes just 1.5 kilowatt-hours (5.4 MJ) of energy to rotate the Wheel -roughly the same as boiling eight small domestic kettles of water.
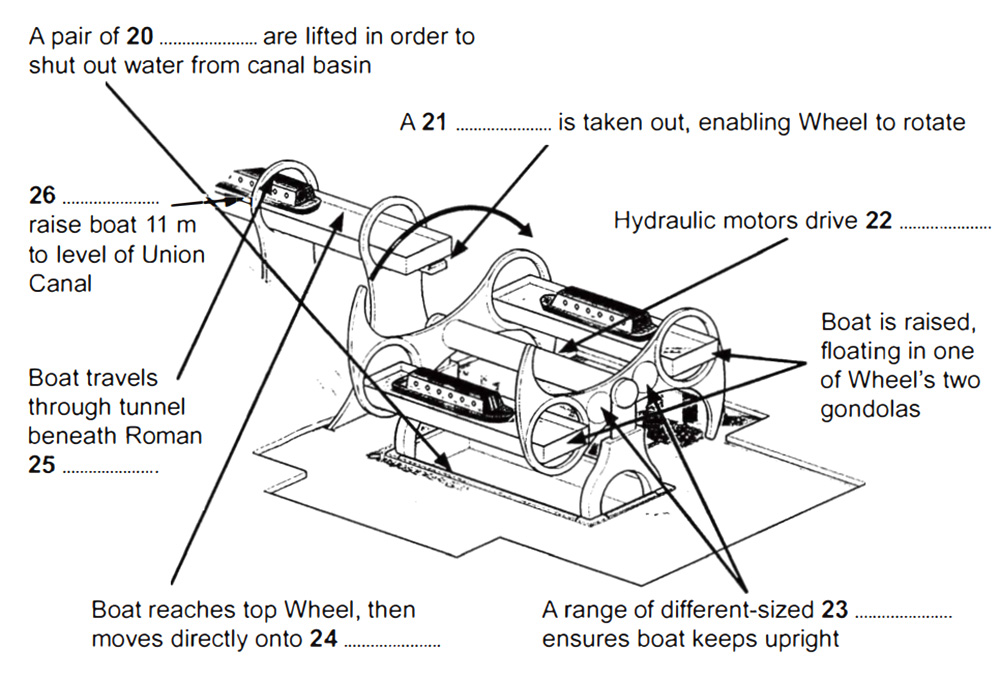
Boats needing to be lifted up enter the canal basin at the level of the Forth & Clyde Canal and then enter the lower gondola of the Wheel. Two hydraulic steel gates are raised, so as to seal the gondola off from the water in the canal basin. The water between the gates is then pumped out. A hydraulic clamp, which prevents the arms of the Wheel moving while the gondola is docked, is removed, allowing the Wheel to turn. In the central machine room an array of ten hydraulic motors then begins to rotate the central axle. The axle connects to the outer arms of the Wheel, which begin to rotate at a speed of 1/8 of a revolution per minute. As the wheel rotates, the gondolas are kept in the upright position by a simple gearing system. Two eight-metre-wide cogs orbit a fixed inner cog of the same width, connected by two smaller cogs travelling in the opposite direction to the outer cogs – so ensuring that the gondolas always remain level. When the gondola reaches the top, the boat passes straight onto the aqueduct situated 24 metres above the canal basin.
The remaining 11 metres of lift needed to reach the Union Canal is achieved by means of a pair of locks. The Wheel could not be constructed to elevate boats over the full 35-metre difference between the two canals, owing to the presence of the historically important Antonine Wall, which was built by the Romans in the second century AD. Boats travel under this wall via a tunnel, then through the locks, and finally on to the Union Canal.
Questions 14-19
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 2?
In boxes 14-19 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
14 The Falkirk Wheel has linked the Forth & Clyde Canal with the Union Canal for the first time in their history.
15 There was some opposition to the design of the Falkirk Wheel at first.
16 The Falkirk Wheel was initially put together at the location where its components were manufactured.
17 The Falkirk Wheel is the only boat lift in the world which has steel sections bolted together by hand.
18 The weight of the gondolas varies according to the size of boat being carried.
19 The construction of the Falkirk Wheel site took into account the presence of a nearby ancient monument.
Questions 20-26
Label the diagram below.
Choose ONE WORD from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 20-26 on your answer sheet.
How a boat is lifted on the Falkirk Wheel
READING PASSAGE 3
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 27-40 which are based on Reading Passage 3 below.
Reducing the Effects of Climate Change
Mark Rowe reports on the increasingly ambitious geo-engineering projects being explored by scientists
A
Such is our dependence on fossil fuels, and such is the volume of carbon dioxide already released into the atmosphere, that many experts agree that significant global warming is now inevitable. They believe that the best we can do is keep it at a reasonable level, and at present the only serious option for doing this is cutting back on our carbon emissions. But while a few countries are making major strides in this regard, the majority are having great difficulty even stemming the rate of increase, let alone reversing it. Consequently, an increasing number of scientists are beginning to explore the alternative of geo-engineering — a term which generally refers to the intentional large-scale manipulation of the environment. According to its proponents, geo-engineering is the equivalent of a backup generator: if Plan A – reducing our dependency on fossil fuels – fails, we require a Plan B, employing grand schemes to slow down or reverse the process of global warming.
B
Geo-engineering; has been shown to work, at least on a small localised scale. For decades, MayDay parades in Moscow have taken place under clear blue skies, aircraft having deposited dry ice, silver iodide and cement powder to disperse clouds. Many of the schemes now suggested look to do the opposite, and reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the planet. The most eye-catching idea of all is suggested by Professor Roger Angel of the University of Arizona. His scheme would employ up to 16 trillion minute spacecraft, each weighing about one gram, to form a transparent, sunlight-refracting sunshade in an orbit 1.5 million km above the Earth. This could, argues Angel, reduce the amount of light reaching the Earth by two per cent.
C
The majority of geo-engineering projects so far carried out — which include planting forests in deserts and depositing iron in the ocean to stimulate the growth of algae – have focused on achieving a general cooling of the Earth. But some look specifically at reversing the melting at the poles, particularly the Arctic. The reasoning is that if you replenish the ice sheets and frozen waters of the high latitudes, more light will be reflected back into space, so reducing the warming of the oceans and atmosphere.
D
The concept of releasing aerosol sprays into the stratosphere above the Arctic has been proposed by several scientists. This would involve using sulphur or hydrogen sulphide aerosols so that sulphur dioxide would form clouds, which would, in turn, lead to a global dimming. The idea is modelled on historic volcanic explosions, such as that of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in 1991, which led to a short-term cooling of global temperatures by 0.5 °C. Scientists have also scrutinised whether it’s possible to preserve the ice sheets of Greenland with reinforced high-tension cables, preventing icebergs from moving into the sea. Meanwhile in the Russian Arctic, geo-engineering plans include the planting of millions of birch trees. Whereas the -regions native evergreen pines shade the snow an absorb radiation, birches would shed their leaves in winter, thus enabling radiation to be reflected by the snow. Re-routing Russian rivers to increase cold water flow to ice-forming areas could also be used to slow down warming, say some climate scientists.
E
But will such schemes ever be implemented? Generally speaking, those who are most cautious about geo-engineering are the scientists involved in the research. Angel says that his plan is ‘no substitute for developing renewable energy: the only permanent solution’. And Dr Phil Rasch of the US-based Pacific Northwest National Laboratory is equally guarded about the role of geo-engineering: ‘I think all of us agree that if we were to end geo-engineering on a given day, then the planet would return to its pre-engineered condition very rapidly, and probably within ten to twenty years. That’s certainly something to worry about.’
F
The US National Center for Atmospheric Research has already suggested that the proposal to inject sulphur into the atmosphere might affect rainfall patterns across the tropics and the Southern Ocean. ‘Geo-engineering plans to inject stratospheric aerosols or to seed clouds would act to cool the planet, and act to increase the extent of sea ice,’ says Rasch. ‘But all the models suggest some impact on the distribution of precipitation.’
G
‘A further risk with geo-engineering projects is that you can “overshoot”,’ says Dr Dan Hunt, from the University of Bristol’s School of Geophysical Sciences, who has studied the likely impacts of the sunshade and aerosol schemes on the climate. ‘You may bring global temperatures back to pre-industrial levels, but the risk is that the poles will still be warmer than they should be and the tropics will be cooler than before industrialisation.’ To avoid such a scenario,” Hunt says, “Angel’s project would have to operate at half strength; all of which reinforces his view that the best option is to avoid the need for geo-engineering altogether.”
H
The main reason why geo-engineering is supported by many in the scientific community is that most researchers have little faith in the ability of politicians to agree – and then bring in — the necessary carbon cuts. Even leading conservation organisations see the value of investigating the potential of geo-engineering. According to Dr Martin Sommerkorn, climate change advisor for the World Wildlife Fund’s International Arctic Programme, ‘Human-induced climate change has brought humanity to a position where we shouldn’t exclude thinking thoroughly about this topic and its possibilities.’
Questions 27-29
Reading Passage 3 has eight paragraphs A-H
Which paragraph contains the following information?
Write the correct letter, A-H, in boxes 27-29 on your answer sheet.
27 mention of a geo-engineering project based on an earlier natural phenomenon
28 an example of a successful use of geo-engineering
29 a common definition of geo-engineering
Questions 30-36
Complete the table below.
Choose ONE WORD from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 30-36 on your answer sheet.
GEO-ENGINEERING PROJECTS
|
Procedure |
Aim |
|
put a large number of tiny spacecraft into orbit far above Earth |
to create a 30………….. that would reduce the amount of light reaching Earth |
|
place 31…………… in the sea |
to encourage 32…………… to form |
|
release aerosol sprays into the stratosphere |
to create 33……………. that would reduce the amount of light reaching Earth |
|
fix strong 34…………… to Greenland ice sheets |
to prevent icebergs moving into the sea |
|
plant trees in Russian Arctic that would lose their leaves in winter |
to allow the 35…………… to reflect radiation |
|
change the direction of 36…………… |
to bring more cold water into ice-forming areas |
Questions 37-40
Look at the following statements (Questions 37-40) and the list of scientists below.
Match each statement with the correct scientist, A-D.
Write the correct letter, A-D, in boxes 37-40 on your answer sheet.
List of Scientists
A Roger Angel
B Phil Rasch
C Dan Lunt
D Martin Sommerkorn
37 The effects of geo-engineering may not be long-lasting.
38 Geo-engineering is a topic worth exploring.
39 It may be necessary to limit the effectiveness of geo-engineering projects.
40 Research into non-fossil-based fuels cannot be replaced by geo-engineering.
Passage 1
1. tomatoes
2. urban centres/ centers
3. energy
4. fossil fuel
5. artificial
6. (stacked) trays
7. (urban) rooftops
8. NOT GIVEN
9. TRUE
10. FALSE
11. TRUE
12. FALSE
13. TRUE
Passage 2
14. FALSE
15. NOT GIVEN
16. TRUE
17. NOT GIVEN
18. FALSE
19. TRUE
20. gates
21. clamp
22. axle
23. cogs
24. aqueduct
25. wall
26. locks
Passage 3
27. D
28. B
29. A
30. sunshade
31. iron
32. algae
33. clouds
34. cables
35. snow
36. rivers
37. B
38. D
39. C
40. A
